この記事では、Pythonでモジュールのソースコードを確認する方法を解説します。
プログラミングしているとモジュールのソースコードがどんなものだったか確認したい時がちょくちょくあります。
そんな時はinspectモジュールを使うことで確認することができます。
ソースコード内からモジュールを確認する
それでは、実際にモジュールのソースコードを確認してみましょう!
書式
モジュールや関数などのソースコードを確認するにはinspectモジュールのgetsource()関数を使います。
import inspect
inspect.getsource(オブジェクト)| 引数 | モジュール、クラス、メソッド、関数、トレースバック、フレーム、コードオブジェクトを指定する |
|---|---|
| 戻り値 | ソースコードは文字列で返される |
サンプル
試しにnumpyのソースコードを確認してみましょう!
import inspect
import numpy
print(inspect.getsource(numpy))実行結果
"""
NumPy
=====
Provides
1. An array object of arbitrary homogeneous items
2. Fast mathematical operations over arrays
3. Linear Algebra, Fourier Transforms, Random Number Generation
How to use the documentation
----------------------------
Documentation is available in two forms: docstrings provided
with the code, and a loose standing reference guide, available from
`the NumPy homepage <https://www.scipy.org>`_.
We recommend exploring the docstrings using
`IPython <https://ipython.org>`_, an advanced Python shell with
TAB-completion and introspection capabilities. See below for further
instructions.
The docstring examples assume that `numpy` has been imported as `np`::
>>> import numpy as np
・
・
・
省略
確認できる標準ライブラリ
標準ライブラリの中にもソースコードを確認できるものがあります。
C言語で書かれているビルトイン(組み込み)モジュールは中身を確認できません。
import sys
import inspect
print(inspect.getsource(sys))実行結果
TypeError: <module 'sys' (built-in)> is a built-in modulePythonで記述されているビルドインモジュールのコードは確認することができます。
import inspect
import bisect
print(inspect.getsource(bisect))実行結果
"""Bisection algorithms."""
def insort_right(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):
"""Insert item x in list a, and keep it sorted assuming a is sorted.
If x is already in a, insert it to the right of the rightmost x.
Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound the
slice of a to be searched.
"""
lo = bisect_right(a, x, lo, hi)
a.insert(lo, x)
def bisect_right(a, x, lo=0, hi=None):
"""Return the index where to insert item x in list a, assuming a is sorted.
The return value i is such that all e in a[:i] have e <= x, and all e in a[i:] have e > x. So if x already appears in the list, a.insert(x) will
insert just after the rightmost x already there.
Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound the
slice of a to be searched.
"""
・
・
・
省略中身を取得できるかどうかはsys.builtin_module_namesで確認できる。
import sys
print(sys.builtin_module_names)実行結果
('_abc', '_ast', '_codecs', '_collections', '_functools', '_imp', '_io', '_locale', '_operator', '_peg_parser', '_signal', '_sre', '_stat', '_string', '_symtable', '_thread', '_tracemalloc', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'atexit', 'builtins', 'errno', 'faulthandler', 'gc', 'itertools', 'marshal', 'posix', 'pwd', 'sys', 'time', 'xxsubtype')上記で表示されたモジュールはinspect.getsource()関数ではソースコードを確認することができません。
標準ライブラリのソースコードを確認する
標準ライブラリのソースコードは、公式ドキュメントから確認することができます。
LinkPython 標準ライブラリ — Python ドキュメント
ライブラリ名の下のリンクをクリックします。
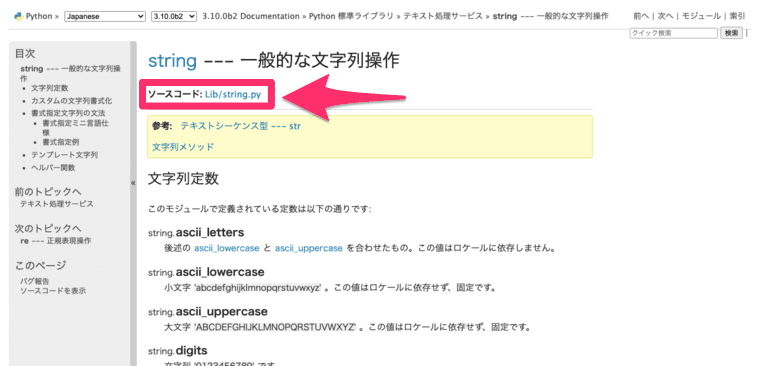
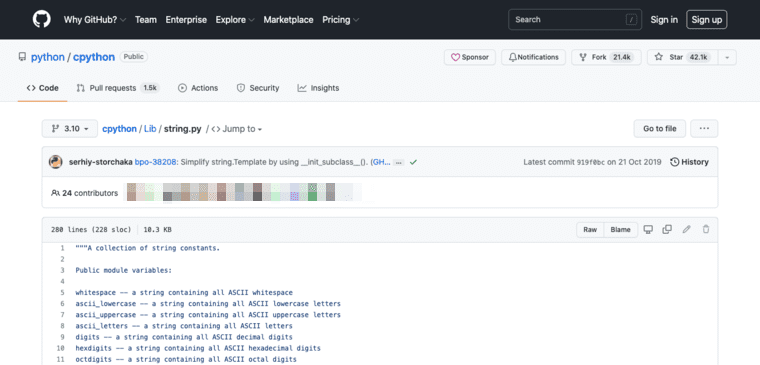
GitHubでソースコードを確認することができます。
まとめ
この記事では、モジュールのソースコードを確認する方法を解説しました。
inspectモジュールのgetsource()関数を使うことでモジュール以外にも様々なソースコードを確認することができます。
とても便利なので頭の片隅に入れておきましょう!
それでは今回の内容はここまでです。ではまたどこかで〜( ・∀・)ノ














